For generations farmers have walked their fields investigating crops manually for signs of stress or disease. This traditional, labor intensive method is time consuming and can be difficult when crop canopies thicken. With the DJI Phantom series, farmers are able to evaluate their crops at scale while simultaneously creating crop maps that help them manage crops and time better. The Phantom series of aircraft are highly portable, and boast industry leading flight times. Equipped with 12 megapixel cameras and up to 4K video they capture clear, detailed images that are essential for analysis and every Phantom is ready to fly out of the box. Aerial thermal imaging has also become an important tool for crop management. It is a non-invasive way to monitor nurseries and greenhouses and even detect plant diseases. Using the DJI Inspire equipped with a DJI Zenmuse XT thermal imaging camera, developed in collaboration with FLIR, all of this important data can be easily captured.
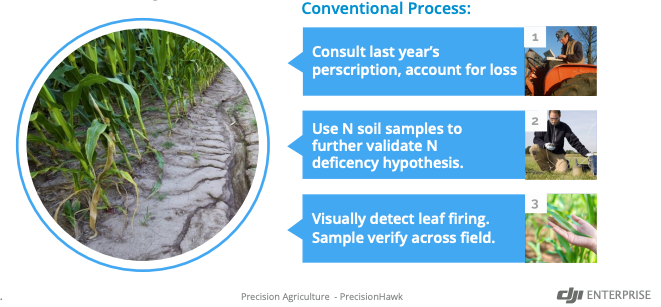
Nitrogen (N) is one of the primary factors that determines realistic yield expectations for corn. Traditionally speaking, farmers tend to counter N deficiency through a process known as ‘side dressing’ and treat their fields uniformly with equal amounts of nitrogen. This method wastes nitrogen on crops that don’t need extra nitrogen and increases operation costs for crop growers.
By using the Smarter Farming Package developed by DJI and PrecisionHawk, drone data can now reveal where farmers need to side dress their crops. Leveraging drone technology allows growers to make precise management decisions that can greatly impact their bottom line at the end of the season.
After ground-truthing a sample area and consulting their agronomist, those corn
farmers had a complete picture of where N needed to be applied.
Furthermore, the entire process of drone flight, data upload, and analysis to N application was completed in just two days, as opposed to using the traditional approach, which took one week.

To find out their actual N deficiency rates and locations, corn farmers and their teams flew DJI’s Matrice 100 drone at the start of V4 in mid-June, equipped with DJI’s Zenmuse X3 multispectral sensor, which is able to record blue, green, and near-infrared bands.





